Loculated Pleural Effusion | If none is present the fluid is virtually always a transudate. Learn about different types of pleural effusions, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. Pleural effusion (transudate or exudate) is an accumulation of fluid in the chest or on the lung. The pleural fluid may be classified as a transudate or an exudate, depending on the etiology. Learn about pleural effusion (fluid in the lung) symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain.
Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. A role in selected clinical circumstances. Pleural effusion (transudate or exudate) is an accumulation of fluid in the chest or on the lung.

It can also be life threatening. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. Pleural fluid/serum ldh ratio >0.6. Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from disruption of the homeostatic forces responsible for the. In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Learn about pleural effusion including causes of pleural effusion. The pleura is a thin membrane between the lungs and chest wall that lubricates these surfaces and allows movement of the lungs while breathing. ✓ pleural effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. More than one half of these massive. Not respond to chest tube and antibiotics. A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural. Pleural fluid ldh > two thirds of upper limit for serum ldh. Pleural fluid/serum ldh ratio >0.6. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion.

The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural. In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed. Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity between the lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity (i.e., the visceral and parietal pleurae). Pleural effusions can loculate as a result of adhesions. It can result from pneumonia and many other conditions. It can also be life threatening. A role in selected clinical circumstances. Pleural fluid/serum ldh ratio >0.6. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis. A pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid within the pleural space. ✓ pleural effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
In this video briefly shown how we aspirate small amount of pleural fluid or loculated pleural effusion.for more videos please subscribe the channel.if you. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion. Pleural fluid/serum protein ratio >0.5. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural.
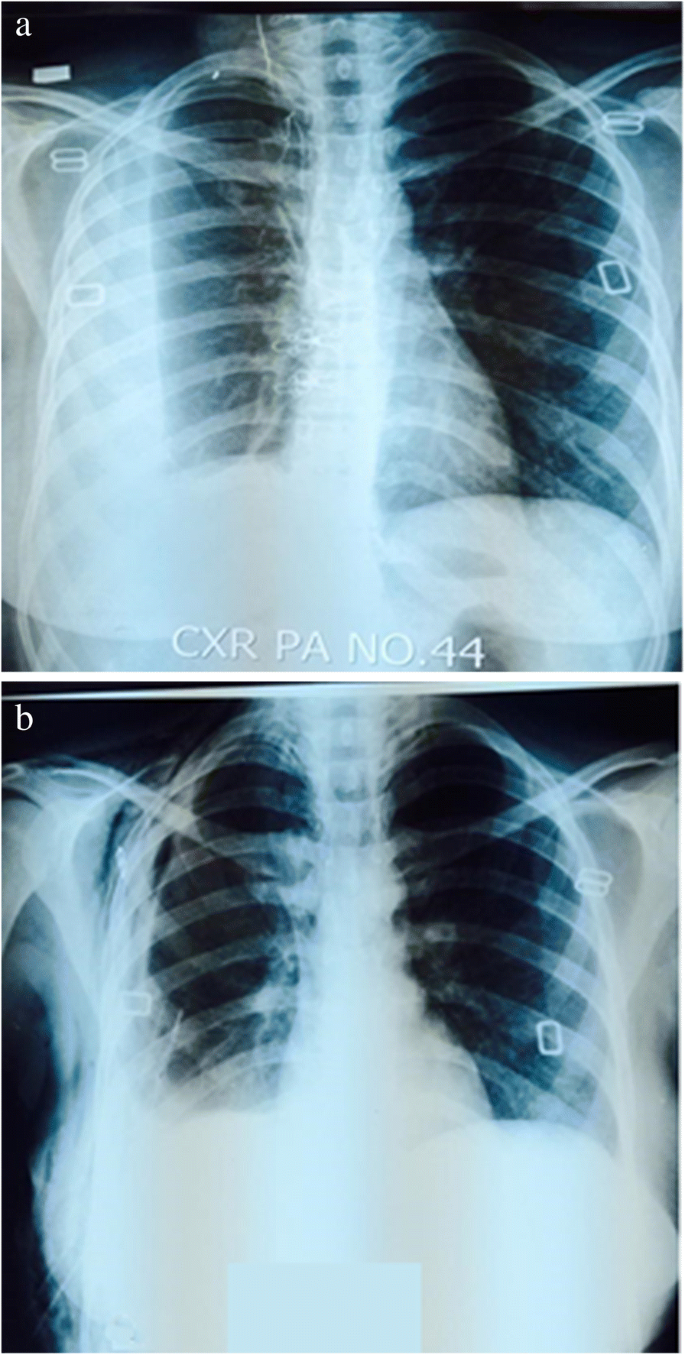
In addition, a diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis of a l > r pleural effusion was performed. Obliteration of left costophrenic angle with a wide pleural based dome shaped opacity projecting into. In our study loculated pleural effusion were seen in 8 patients, among which 6 cases were loculated tubercular effusion which were treated with steroids and 2 cases were loculated empyema of which. Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. Pleural fluid/serum ldh ratio >0.6. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural. Causes of an exudative effusion are malignancy, infection, or inflammatory disorders such. Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from disruption of the homeostatic forces responsible for the. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis. However, patients can also have neutrophilic loculated. Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural. A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. A role in selected clinical circumstances.
Loculated Pleural Effusion: Pleural fluid ldh > two thirds of upper limit for serum ldh.